Midwives vs OB-GYN: Which Is Right for Your Pregnancy?
When it comes to pregnancy care, expectant mothers often face the decision of whether to choose a midwife or an obstetrician-gynaecologist (OB-GYN) for their birth experience. Both midwives and OB-GYNs play important roles in maternal healthcare, offering distinct services and philosophies of care. Understanding the differences between the two, the benefits of each and the unique roles they play during pregnancy and childbirth is essential for making an informed choice.
Table of Contents
- What Is the Difference Between a Midwife and an OB-GYN?
- Midwife Care During Pregnancy
- OB-GYN Birth Plan Choices
- Benefits of Midwives for Pregnancy
- Advantages of OB-GYNs in Childbirth
- Midwife vs OB-GYN Safety
- What Does a Midwife Do During Labour?
- What Does an OB-GYN Do?
- How Long Does a Midwife Stay After Birth?
- Disadvantages of Having a Midwife
What Is the Difference Between a Midwife and an OB-GYN?
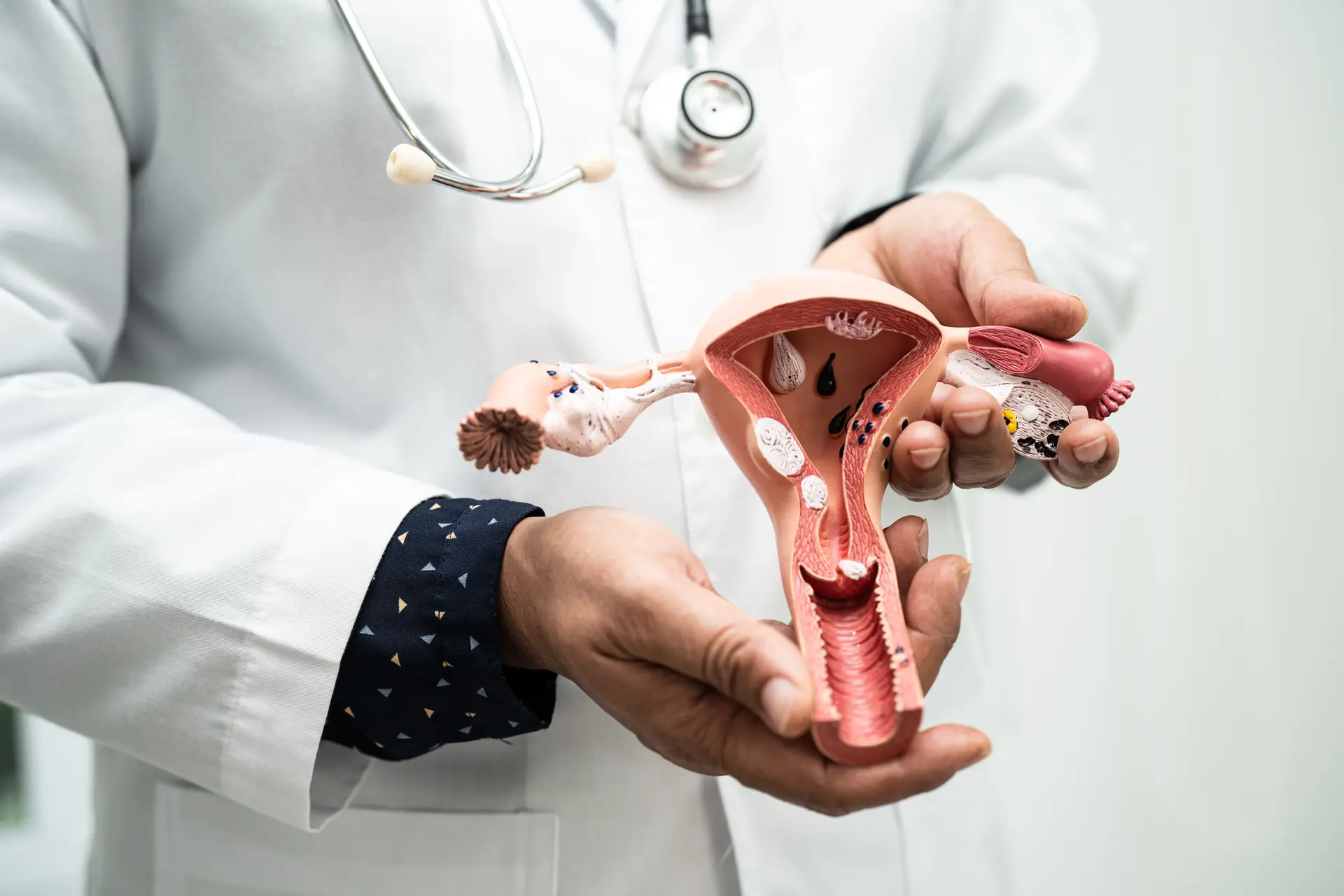
The primary distinction between a midwife vs OB-GYN lies in their education, training and scope of practice. An OB-GYN is a medical doctor with extensive training in obstetrics (the care of pregnant women) and gynaecology (the medical care of the female reproductive system). OB-GYNs attend medical school and complete residency training in obstetrics and gynaecology, equipping them to manage both high-risk and low-risk pregnancies, perform surgeries and handle complications such as preeclampsia, breech births or caesarean sections.
On the other hand, a midwife is a trained professional who provides prenatal, labour and postnatal care, but typically without the use of medical interventions such as surgery or medications. Midwives often hold degrees or certifications in midwifery, and many have training in midwife care during pregnancy, including prenatal health, childbirth support and breastfeeding advice. While midwives are skilled in supporting natural births, they usually work in conjunction with medical doctors like OB-GYNs if complications arise. Midwives are more likely to provide care in home births or birthing centres, as opposed to hospitals, though some midwives do work in hospital settings as well.
Midwife Care During Pregnancy
One of the most attractive features of midwife care during pregnancy is the emphasis on personal attention and continuous support. Midwives typically spend more time with their patients during prenatal visits than OB-GYNs, fostering a more intimate and holistic approach to pregnancy care. During prenatal visits, midwives focus on educating expectant mothers, providing emotional support and ensuring the health of both mother and baby.
Midwives generally encourage more natural and non-invasive approaches to pregnancy care, promoting healthy lifestyle changes, dietary guidance and natural pain relief techniques. For women who desire a birth plan focused on minimal medical intervention, midwives’ prenatal care may be more aligned with their preferences. Midwives are also trained to monitor the progress of the pregnancy, perform routine health screenings and detect any early signs of complications.
OB-GYN Birth Plan Choices
In contrast, OB-GYN birth plan choices tend to provide a wider range of medical interventions. OB-GYNs are trained to handle both routine and high-risk pregnancies and can offer a variety of childbirth options, including the use of epidurals, assisted deliveries with forceps or vacuum and caesarean sections. For mothers who desire a birth with more medical interventions or who are carrying high-risk pregnancies, an OB-GYN might be the preferred choice.
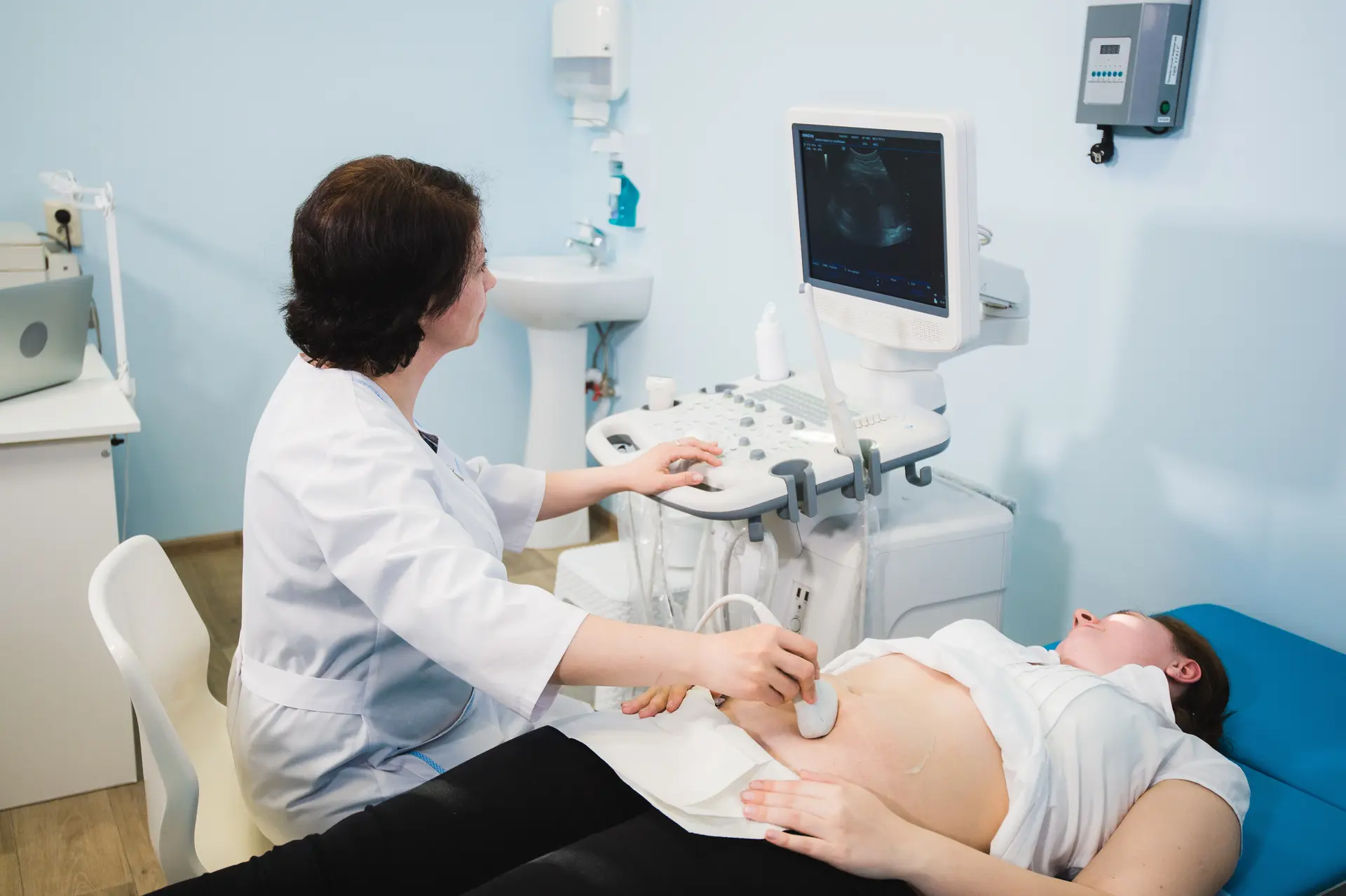
OB-GYNs also have the ability to perform ultrasounds, manage complications like gestational diabetes or hypertension and provide care for women who are expecting multiples. Additionally, OB-GYNs are often the primary providers for women who experience complications or have pre-existing medical conditions that require specialist care, such as heart disease or diabetes.
Benefits of Midwives for Pregnancy
The benefits of midwives for pregnancy can be particularly appealing for women seeking a more personalised, supportive approach to childbirth. Midwives are trained to provide emotional care and practical guidance, which can help reduce anxiety and build confidence in the mother’s ability to handle childbirth. Many women who choose midwives value the close, one-on-one care they receive, and the reassurance of having a skilled professional by their side throughout the pregnancy and delivery.
Midwives are also often associated with lower intervention rates, such as fewer caesarean sections, fewer epidurals and less frequent use of forceps or vacuum extractions. This can lead to a more natural birth experience, which many women find empowering. Furthermore, midwives tend to spend more time educating their patients on prenatal care, breastfeeding and newborn care, which can be beneficial for first-time mothers.
Advantages of OB-GYNs in Childbirth
While midwives’ prenatal care focuses on natural childbirth and minimal medical intervention, OB-GYNs in childbirth bring a different set of advantages to the table, especially in high-risk situations. OB-GYNs are trained to identify and manage complications that may arise during pregnancy and labour, such as preeclampsia, foetal distress and problems with the placenta. If any medical complications arise, OB-GYNs are well-equipped to offer interventions such as caesarean sections or assisted births, ensuring the safety of both mother and baby.
Moreover, OB-GYNs offer a broader spectrum of medical services, such as fertility treatments, diagnostic tests and gynaecological surgeries, making them an invaluable part of a woman’s healthcare team. For women with pre-existing health conditions, an OB-GYN’s expertise in managing complex pregnancies is crucial. OB-GYNs also have access to advanced technology, including ultrasound machines, which can provide detailed insights into the health of the baby and mother during pregnancy.
Midwife vs OB-GYN Safety
One of the primary concerns for expectant mothers is safety, and the decision between midwife vs OB-GYN safety can depend on individual health risks and the type of birth experience desired. Studies have shown that for low-risk pregnancies, midwives are just as capable of delivering babies safely as OB-GYNs, and in some cases, midwives may even have lower rates of interventions like caesarean sections. However, for women with high-risk pregnancies or pre-existing health conditions, OB-GYNs are more equipped to handle potential complications and medical emergencies.
It’s important to note that midwives are trained to recognise when complications arise and to transfer care to an OB-GYN if necessary. In fact, many midwives work in collaboration with OB-GYNs to ensure that the mother and baby receive the best possible care. Ultimately, both midwives and OB-GYNs prioritise the health and safety of the mother and baby, but their methods and approaches to care can differ depending on the pregnancy.
What Does a Midwife Do During Labour?
During labour, a midwife’s role is to provide continuous emotional and physical support, monitor the progress of labour and assist the mother in managing pain and discomfort. Midwives are skilled in natural pain relief techniques, such as breathing exercises, water immersion and massage. They also provide reassurance and guidance, helping the mother stay calm and focused during the process.
Midwives are trained to manage normal deliveries, but if complications arise, they are equipped to call for medical assistance from an OB-GYN or transfer the mother to a hospital. Midwives also assist with immediate post-birth care, including ensuring that the baby is breathing and feeding properly, and providing guidance on breastfeeding and newborn care.
What Does an OB-GYN Do?
An OB-GYN plays a more medicalised role in pregnancy care, offering both prenatal and postnatal care, as well as performing deliveries. They are trained to monitor the health of the mother and baby, conduct diagnostic tests such as ultrasounds and blood tests and handle complications that may arise during pregnancy or childbirth. OB-GYNs are also responsible for performing caesarean sections, managing epidurals and overseeing complex pregnancies that require specialised care.
OB-GYNs can perform ultrasounds to check the baby’s growth and development, as well as detect potential abnormalities. They also manage high-risk pregnancies, ensuring that both the mother and baby receive the necessary medical care.
How Long Does a Midwife Stay After Birth?
After the birth, a midwife typically stays with the new mother for several hours to ensure that both mother and baby are stable. They provide assistance with breastfeeding, monitor the mother’s recovery and ensure that the baby is feeding well. In some cases, midwives will schedule follow-up visits to check on the mother and baby in the days or weeks following the birth.
Midwives are often involved in postnatal care, helping the new mother adjust to life with a newborn, offering advice on infant care and providing emotional support as the mother recovers from childbirth.
Disadvantages of Having a Midwife
While there are many benefits of midwives for pregnancy, there are also some disadvantages of having a midwife. For example, midwives may not be equipped to handle high-risk pregnancies or complications during labour. Women with certain medical conditions, such as gestational diabetes or preeclampsia, may require the expertise of an OB-GYN to manage these issues. Additionally, midwives may not have access to the same medical technologies, such as ultrasounds or monitoring equipment, that OB-GYNs do. If complications arise, there may be a need to transfer care to a hospital or OB-GYN, which can be stressful and time-consuming.
Conclusion
Choosing between a midwife and OB-GYN is a highly personal decision, and one that depends on the type of pregnancy, health considerations and preferences for the birth experience. Midwives are an excellent choice for women seeking a natural, holistic approach to pregnancy and childbirth, while OB-GYNs are ideal for those with high-risk pregnancies or those seeking more medical interventions. Ultimately, the best choice will depend on the mother’s individual needs, and many women find that a combination of both midwife care and OB-GYN expertise provides the best balance of personalised care and medical safety.
Whether opting for midwife care during pregnancy or the medical expertise of an OB-GYN, the most important factor is ensuring that the mother and baby receive the best possible care, tailored to their unique needs. By understanding the roles of each professional, women can make a more informed decision about their pregnancy care.
Whether you’re considering a midwife or an OB-GYN for your pregnancy journey, speak to a Lenmed maternity care team, including experienced midwives and obstetricians, to help you make the right choice for your birth plan and prenatal care.
For more information, please contact:
Discipline: Nephrologist
Hospital: The Bank Hospital
Telephone: +233 20 886 7829
Discipline: Gynaecologist, Obstetrician
Hospital: The Bank Hospital
Telephone: +233 26 462 5142
Discipline: Gynaecologist, Obstetrician
Hospital: Randfontein Private Hospital
Telephone: +27 87 287 5215